Determine a the Principal Stresses and B the Maximum
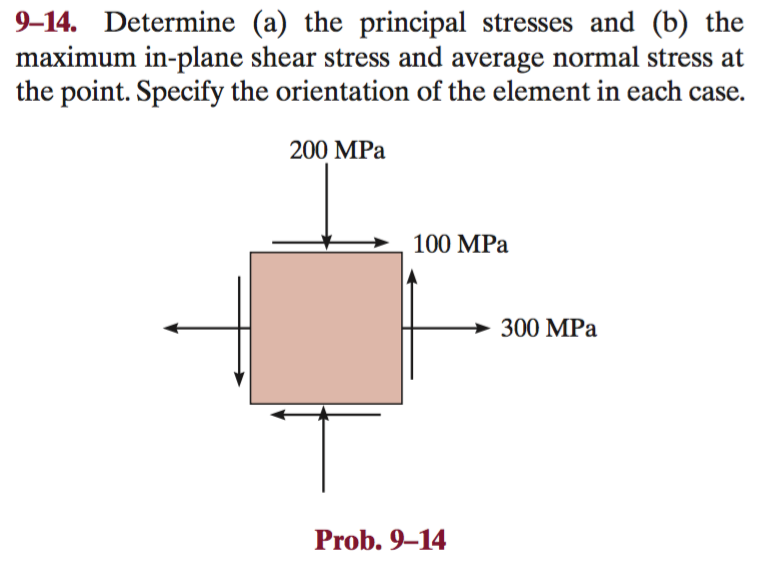
Determine a the principal stress and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point. 1 Answer to A.
Solved Determine A The Principal Stresses And B The Chegg Com
Here we are looking that is pin and its left here and the roller support here as.
. Mechanics of Materials Instructor Solutions Manual EXP-4667 Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress. A Determine the principal stresses and the maximum in-plane shear stress acting at the point. For the principal stress tensor above.
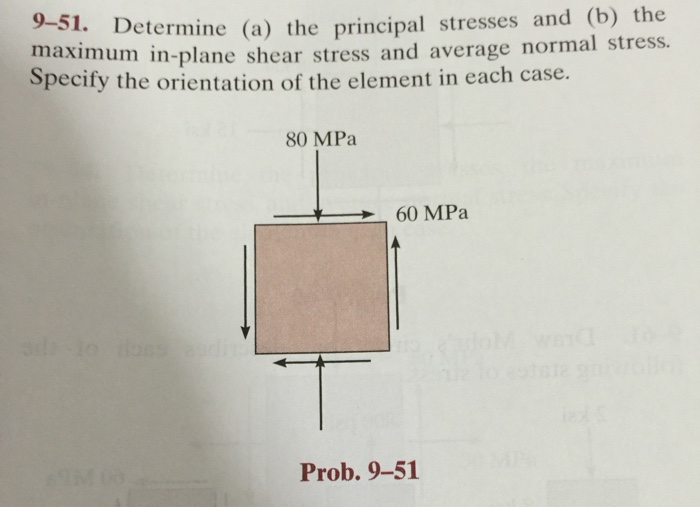
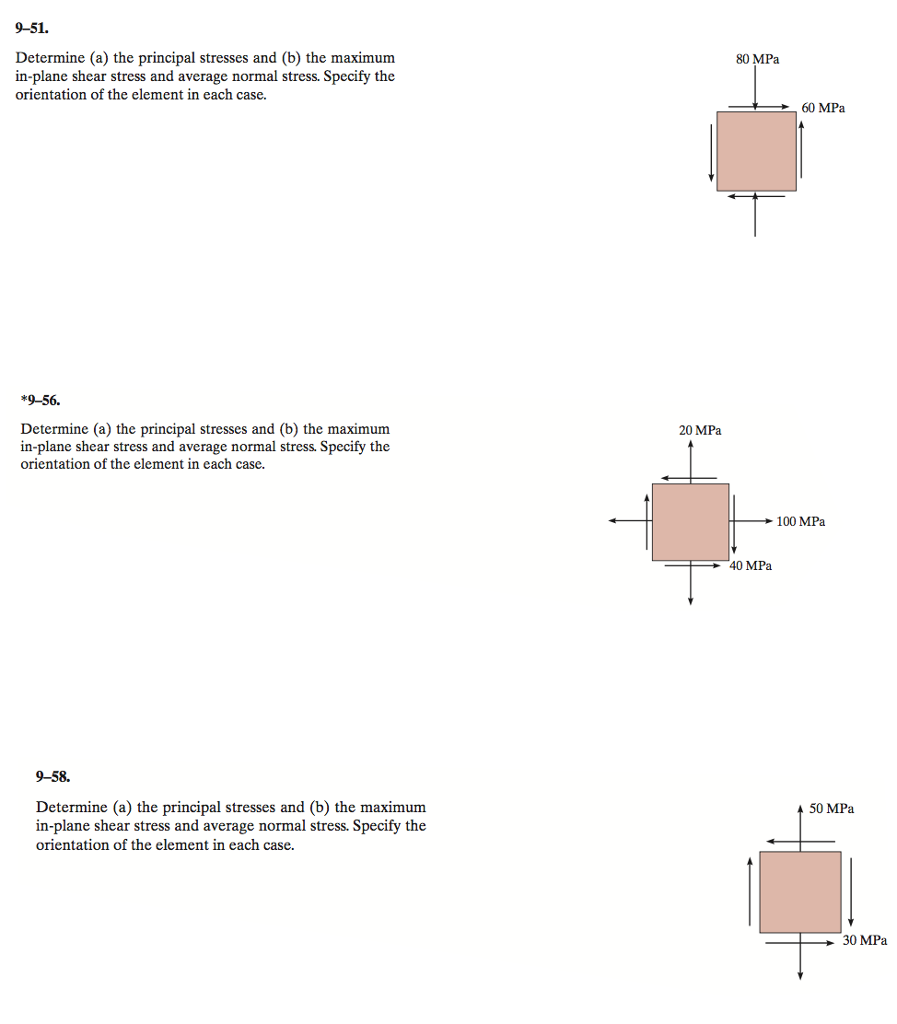
60 MPa 100 MPa 48 MPa For the state of plane stress shown determine a the principal stresses and their principal planes b the maximum shear stress and the corresponding normal stress. 80 MPa Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress. 52 σ 1 2 σx σy 2 σx σy 22 τ.
The maximum shear stress at any point is easy to calculate from the principal stresses. Determine the state of stress on points a and b on cross section B. First week only 499.
Represent the state of stress at points a and b in three-dimensional differential stress elements. Is the minimum stress Note that it is possible that 𝜎𝜎. Bx500 N By750 N.
Is the maximum stress and 𝜎𝜎. B Show these stresses on an appropriate sketch eg see Figure 1215 or Figure 1216 c Compute the absolute shear stress at the point. 𝑝 10 MPaand 𝜎𝜎.
Principal Stress Element. P1 45602 45-602 cos 2a 30 sin2a 53 MPa. Solve the problem using the formula comparing to Mohrs Circle.
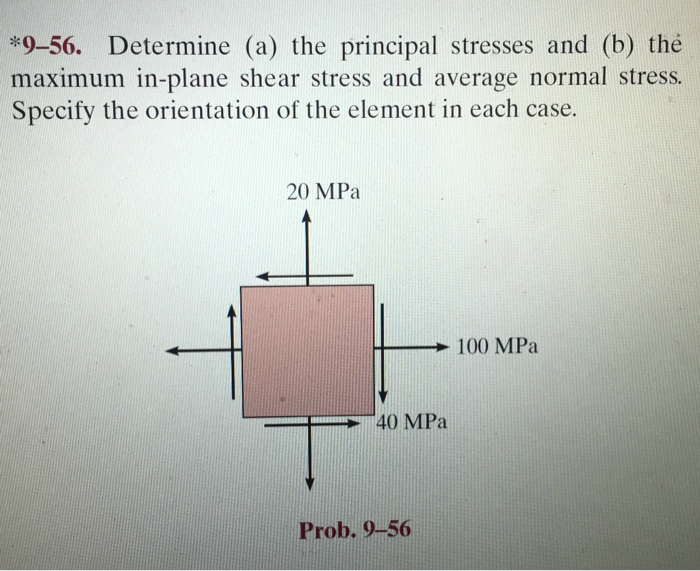
Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress 20 MPа 100 MPa 40 MPa Prob. We always use the convention 𝜎𝜎. 𝑝 20 MPa.
Specify the orientation of the element in each case. And this problem we have Ill be him. Rankin stated max principal stress theory as follows- a material fails by fracturing when the largest principal stress exceeds the ultimate strength σ.
A The principal planes. The maximum shear stress at any point is easy to calculate from the principal stresses. A principal stress element has.
This will and lets see. The state of stress at a point is shown on the element. 956 This problem has been solved.
Specify the orientation of the element in each case. 160 MPa 120 MPa. In a simple tension test.
Mohrs Circle for Plane Stress. Specify the orientation of the element in each case. B The principal stresses.
Specify the orientation of the element in each case. Determine the principal stresses and the absolute maximum shear stress at point b. Determine the equivalent state of stress if an element is oriented 25.
The maximum shear always occurs in a coordinate system orientation that is rotated 45 from the principal coordinate system. Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress. The maximum principal stress criterion.
A 1487 degree. Make sure you identify the plane corresponding to the state of plane stress 13 x x F x x M x yz M. B Shear stress in plane.
The maximum shear always occurs in a coordinate system orientation that is rotated 45 from the principal coordinate system. 𝐌𝐁Mx My Mz 𝒛 Using force balance we get. 60 MPa 30 MPa 45 MPa Ans.
Specify the orientation of the element in each case. Solution for Determine maximum shear stress if maximum principal stress is 4 MPa and minimum principal stress is -4 MPa. The transformation equations for plane stress can be represented in a graphical format known as Mohrs circle.
Sqrt 45- -6022 30 605 MPa. Average 45- -602 -75 MPa. The state of stress at a point is shown on the element.
Calculate the stress at the point of interest due to each internal resultant Combine the individual stresses and draw the stress element For example Use Mohrs circle to determine the principal stresses max shear stress etc. Is greatest in. Start your trial now.
Normal and shear stresses acting on horizontal and vertical planes at the point are shown. Specify the orientation of the element in each case. U s -301 and 599 t max in-plane s avg -750 MPa 605 MPa u p1 149 and u p2 -751 s 1 530 MPa s.
It is simply tau_max sigma_max - sigma_min over 2 This applies in both 2-D and 3-D. C The maximum shear stress and the corresponding normal stress. 20 MPa 100 MPa 40 MPa Prob.
The principal stresses maximum and minimum normal stresses and the orientation θ of the element are obtained by differentiating σ x and σ y in Eq. Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point. Counterclockwise from the element shown.
Sketch the results on each element. That is at the onset of facture σ. Determine a the principal stresses and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress.
51 with respect to θ which yields the following results. It is simply tau_max sigma_max - sigma_min over 2 This applies in both 2-D and 3-D. Determine a the principal stress and b the maximum in-plane shear stress and average normal stress at the point.
This representation is useful in visualizing the relationships. Specify the orientation of the element in.
Solved Determine A The Principal Stresses And B The Chegg Com

Solved 9 51 Determine A The Principal Stresses And B Chegg Com
Solved Determine A The Principal Stresses And B The Chegg Com
No comments for "Determine a the Principal Stresses and B the Maximum"
Post a Comment